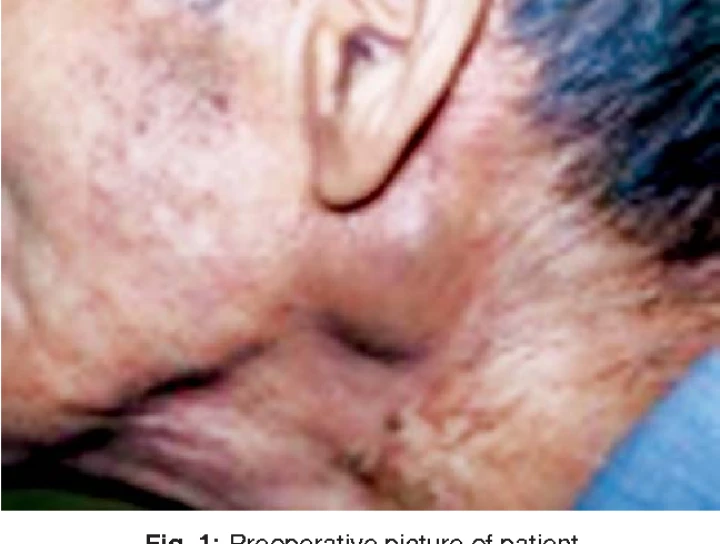
**Extraparotid Warthin's tumor** presents a diagnostic challenge due to its unusual location outside the parotid gland and its resemblance to other neoplastic or non-neoplastic conditions. Warthin's tumor, also known as **papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum**, is typically a benign salivary gland tumor usually found in the parotid gland. When it occurs outside the parotid gland, diagnosing it can be complex. Here's a comprehensive overview of extraparotid Warthin's tumor, its diagnostic challenges, and approaches to management:
### Overview of Warthin's Tumor
**1. **Typical Presentation:**
- **Location:** Warthin's tumor is most commonly found in the parotid gland, particularly in the tail of the gland.
- **Demographics:** It predominantly affects middle-aged to elderly males and is often bilateral.
**2. **Histology:**
- **Features:** Characterized by cystic spaces filled with a serous fluid, surrounded by a double layer of columnar or cuboidal epithelial cells and abundant lymphoid stroma.
### Extraparotid Warthin's Tumor
**1. **Definition and Location:**
- **Extraparotid:** Refers to Warthin’s tumor occurring outside the parotid gland. It can appear in other salivary glands or in ectopic locations, such as cervical lymph nodes or the nasopharynx.
- **Unusual Sites:** Cases have been reported in the submandibular gland, minor salivary glands, and even in ectopic locations not traditionally associated with Warthin’s tumor.
**2. **Clinical Presentation:**
- **Symptoms:** Depending on the location, symptoms may include a palpable mass, pain, swelling, or pressure symptoms. Symptoms can vary widely and may mimic other conditions, leading to diagnostic confusion.
- **Size and Growth:** The tumor's size and growth pattern can be variable, which complicates diagnosis and treatment planning.
### Diagnostic Challenges
**1. **Clinical Evaluation:**
- **Physical Examination:** Extraparotid Warthin's tumor may present as a mass in the neck or oral cavity. Differentiating it from other neoplasms or non-neoplastic conditions based on clinical examination alone can be challenging.
**2. **Imaging Studies:**
- **Ultrasound:** Useful for initial evaluation to determine the tumor’s location, size, and characteristics. It can help differentiate between solid and cystic masses.
- **CT Scan/MRI:** Provides detailed images of the mass and its relation to surrounding structures. Helps in assessing the extent of the disease and planning surgical interventions.
- **Limitations:** Imaging alone may not be sufficient for definitive diagnosis, especially in extraparotid cases where the tumor might be confused with lymphadenopathy or other tumors.
**3. **Histopathological Diagnosis:**
- **Biopsy:** Fine needle aspiration (FNA) or core needle biopsy may be performed to obtain tissue samples for histopathological examination.
- **Histology:** Requires careful evaluation to confirm the presence of the characteristic cystic and lymphoid stroma features of Warthin’s tumor. Differential diagnosis includes other salivary gland tumors, lymphomas, or metastatic disease.
**4. **Differential Diagnosis:**
- **Lymphoma:** Particularly in cases where the tumor is located in lymph nodes or has significant lymphoid stroma.
- **Other Salivary Gland Tumors:** Such as pleomorphic adenoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, or adenoid cystic carcinoma.
- **Metastatic Disease:** Especially if the tumor is in an atypical location or presents with aggressive features.
### Management and Treatment
**1. **Surgical Intervention:**
- **Surgical Resection:** The primary treatment for extraparotid Warthin’s tumor is surgical excision. Complete removal of the tumor is crucial to prevent recurrence.
- **Challenges:** Surgical approach may vary based on the tumor’s location. For instance, a tumor in the submandibular gland requires careful dissection to avoid damage to surrounding structures.
**2. **Follow-Up and Monitoring:**
- **Post-Surgical Care:** Regular follow-up with imaging and clinical examination is necessary to monitor for any recurrence or complications.
- **Long-Term Prognosis:** Warthin’s tumors are generally benign with a good prognosis after complete excision. However, extraparotid locations may warrant closer monitoring.
### Conclusion
**Extraparotid Warthin's tumor** poses a diagnostic dilemma due to its atypical presentation outside the parotid gland and its potential resemblance to other conditions. Accurate diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and histopathological examination. Management typically involves surgical resection, with follow-up care essential to monitor for recurrence. Awareness of this rare presentation and its differential diagnoses is crucial for timely and effective treatment.


No Any Replies to “Extraparotid Warthin′s Tumor A Diagnostic Dilemma”
Leave a Reply