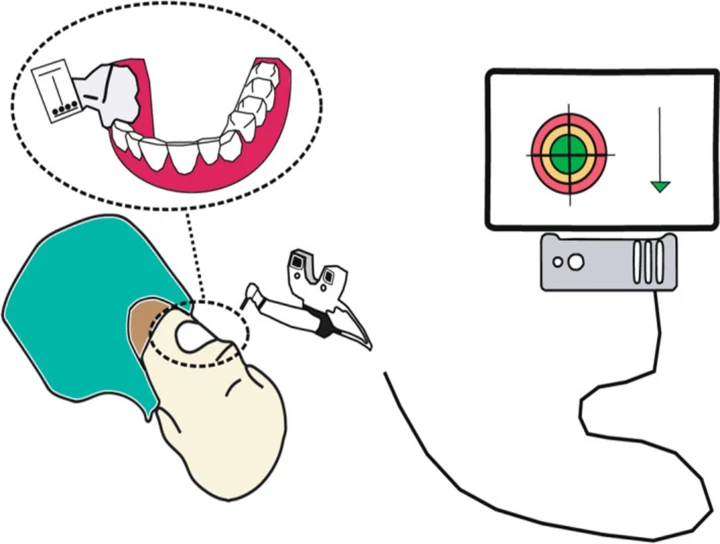
Dynamic navigation scheme: A marker is positioned in the patient's mouth. A stereoscopic camera is connected to a computer. The corresponding software presents the dynamic navigation in real time. The spatial and angular deviation as well as the depth is displayed.
WHAT
IS GUIDED ENDODONTICS?
Guided Endodontics is a novel technique based on CAD-CAM workflow to plan and create 3D printed templates, which aims to guide the access of pulp canals with pathologic anatomy or obliterations.
It is of two types – Static Navigation (uses a template to guide a bur) and Dynamic Navigation (uses a camera and 3D markers which help us to provide information about the axis and depth).
· AUGMENTED REALITY IN DYNAMIC NAVIGATION GUIDED ENDODONTICS
The main limitation of this dynamic navigation system is that the clinician must look at the display rather than direct observing tooth. This problem can be addressed by using a head-mounted display (HMD)-AR system.
Augmented reality (AR) navigation might be the next step towards improving the operator experience with dynamic navigation. The AR approach overlays images, such as radiographic images and navigation paths, with a view of the operative field in a wearable head‐up display or a dedicated microscope. Thus, the operator can simultaneously visualize the operative field and 3D navigation images without having to look up at a display.
· CONCLUSION
AR in Guided Endodontics has the potential to improve the accuracy and safety of root canal treatments while enhancing patients and dentists experience.
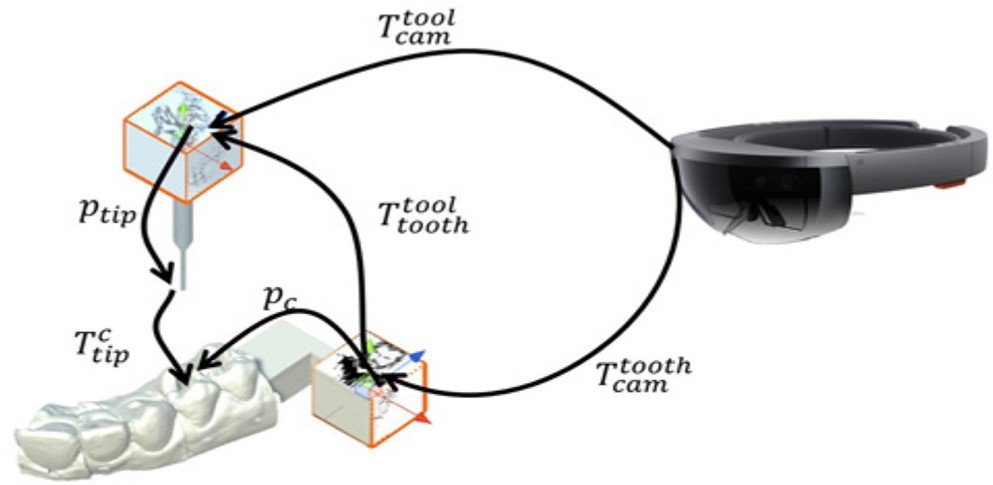
A marker is used for tracking the tooth which is mounted on an adapter that is fixated on the teeth. A second marker is mounted on the handpiece (tool) that the dentist is using for drilling. As one can see both markers are clearly out of the mouth and are visible for tracking purposes.
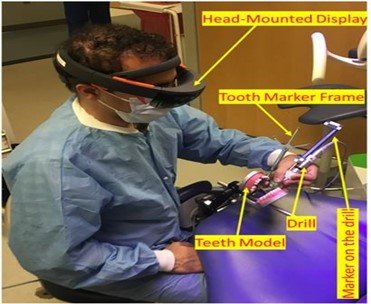
Head Mounted Display -AR
Dynamic Navigation System


No Any Replies to “FUTURE DIRECTIONS OF DYNAMIC NAVIGATION IN GUIDED ENDODONTICS”
Leave a Reply