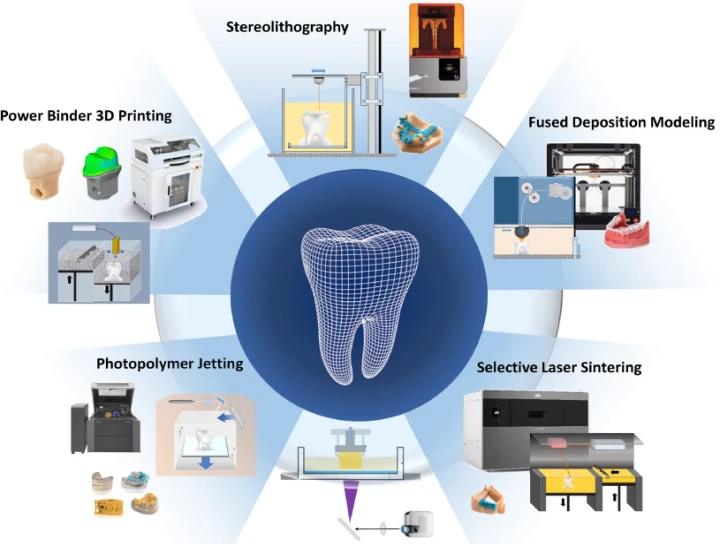
Introduction:
In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a groundbreaking technology with the potential to transform various industries. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing allows the creation of three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on digital designs. This document explores the concept of 3D printing, its applications across industries, and the disruptive impact it has had on traditional manufacturing processes.
Understanding 3D Printing:
3D printing is a process that starts with a digital 3D model of an object, which is then sliced into multiple thin layers. The 3D printer reads these layers and creates the object by depositing or solidifying material layer by layer. Various materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological substances, can be used in the 3D printing process, offering immense versatility.
Disruptive Impact on Manufacturing:
The traditional manufacturing process often involves subtractive methods, where materials are cut or shaped to achieve the desired object. 3D printing, on the other hand, follows an additive approach, eliminating the need for extensive tooling and reducing material waste. This disruptive technology has the potential to reshape the manufacturing landscape by offering numerous advantages, including:
a. Cost-Efficiency: 3D printing enables the production of complex objects without the need for specialized tools or molds, reducing manufacturing costs. It also eliminates the need for large-scale production facilities, allowing decentralized manufacturing.
b. Customization and Personalization: With 3D printing, objects can be easily customized, tailored to individual needs, and produced on-demand. This level of customization revolutionizes product design, allowing for unique and personalized creations.
c. Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing accelerates the product development cycle by enabling rapid prototyping. It allows designers and engineers to quickly iterate and test their designs, reducing time-to-market and fostering innovation.
d. Supply Chain Optimization: 3D printing has the potential to transform supply chains by enabling localized production. This reduces transportation costs, inventory requirements, and dependence on global sourcing.
Applications of 3D Printing:
The impact of 3D printing extends across various industries, including:
a. Healthcare: 3D printing facilitates the creation of patient-specific medical devices, prosthetics, implants, and anatomical models for surgical planning. It has the potential to revolutionize personalized medicine and enhance patient care.
b. Aerospace and Automotive: 3D printing allows the production of lightweight, complex components with optimized designs. It enables the creation of prototypes, spare parts, and low-volume production runs, reducing costs and lead times.
c. Architecture and Construction: 3D printing enables the construction of intricate architectural models, prototypes, and even full-scale structures. It offers the potential for sustainable and cost-effective building solutions.
d. Consumer Goods: 3D printing opens up possibilities for customized consumer products, fashion accessories, jewelry, and home décor items. It empowers individuals to become creators and designers themselves.
Conclusion:
3D printing has emerged as a disruptive technology, revolutionizing manufacturing processes across industries. Its ability to enable cost-efficient production, customization, rapid prototyping, and supply chain optimization has transformed the way objects are designed, produced, and distributed. As this technology continues to advance, its impact on various sectors is poised to grow, ushering in a new era of innovation, sustainability, and personalized manufacturing.


No Any Replies to “3D Printing: Revolutionizing Manufacturing with Disruptive Technologies”
Leave a Reply