ADRENERGIC DRUGS
The Adrenergic drugs are those medications that can stimulate certain nerves of the body. The said action is performed by simulating and stimulating the actions of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine, which are chemical messengers. The drugs have been used in allergic reactions, cardiac arrests and shocks.
Objectives..
· To identify the various actions of adrenergic medications based on the receptor to which they bind.
· To describe the various adverse effects of the drugs based on the binding site.
So how do they work .. ?
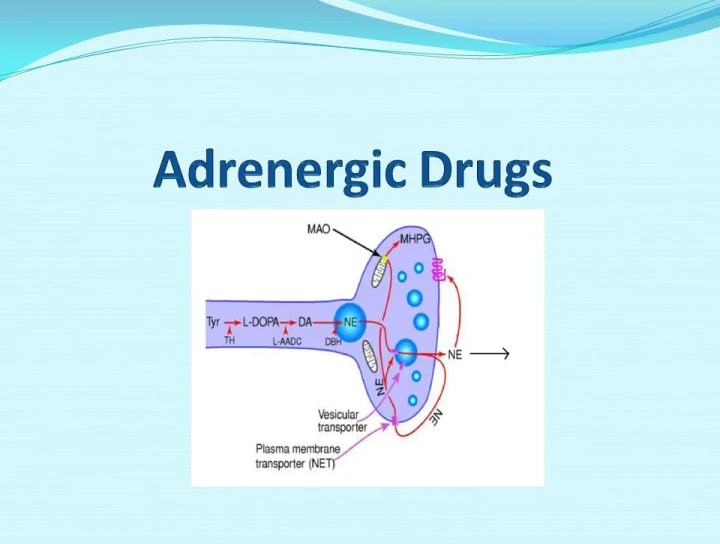
The Adrenergic drugs are a broad class of medications that bind to adrenergic receptors throughout the body. The receptors include alpha 1 & 2, beta 1 & 2.
Direct Acting sympathomimetics imitate normal physiology and directly activate adrenergic receptors. The Alpha 1 agonists contract vascular smooth muscle. The Alpha 2 agonists contract smooth muscle. The Beta 1 agonists increase heart rate. The Beta 2 agonists relax respiratory and uterine smooth muscle.
Indirect Acting adrenergic agonists can stimulate and increase release of neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine from the nerve endings into synapses, and decrease the reuptake of neurotransmitters into the presynaptic nerve. Amphetamines and Cocaine.
Dual acting /Mixed Action stimulate adrenergic receptor sites and release of norepinephrine from nerve endings.
The Application
The drugs are used in cases of hypotension like shock, spinal anaesthesia, prolonging the duration of Local Anaesthetics [ Adrenaline 1 in 200,000 or 100,000], for controlling bleeding of skin and mucous membranes [ Adr 1 in 100,000, Nasal decongestions and Cardiac Arrests to name a few.


No Any Replies to “ADRENERGIC DRUGS”
Leave a Reply